G1 Garlic in Pakistan (لہسن کی کاشت) in Urdu and English

Last updated on July 30th, 2023 at 06:00 pm
Production Plan for NARC G1 Garlic in Pakistan (لہسن کی کاشت). A high value vegetable which is growing popular due to high rates and market.


1



1



Literature by Dr. Mansab Ali Khokhar from Chiniot and Mehr Mushtaq Ahmad from Bahawalpur, Agriculture Experts and Farmers.
Introduction to NARC G1 Garlic in Pakistan (In English):
What is NARC G1 Garlic?
NARC G1 Garlic refers to a specific variety of garlic developed by the National Agricultural Research Center (NARC) in Pakistan. This variety is the result of years of research and breeding efforts aimed at improving garlic cultivation in the country. NARC G1 Garlic is known for its high yield potential, disease resistance, and adaptability to various climate and soil conditions found in Pakistan. It has emerged as a significant agricultural innovation and a game-changer in the garlic industry.
Origins and Development of NARC G1 Garlic:
The development of NARC G1 Garlic began with extensive research and genetic studies conducted by NARC’s team of agricultural scientists and experts. The primary objective was to enhance the yield and quality of garlic to meet the growing demand of the Pakistani population and explore export opportunities. Through a combination of conventional breeding techniques and modern biotechnology, NARC successfully selected and bred garlic strains that exhibited the desired traits, resulting in the creation of NARC Garlic.
Importance of NARC G1 Garlic in Pakistan’s Agriculture:
NARC G1 Garlic holds immense importance for Pakistan’s agricultural sector. Garlic is a staple ingredient in Pakistani cuisine and is also used for medicinal purposes. With the introduction of NARC G1 Garlic, farmers have experienced increased crop yields and improved crop quality, leading to higher profits. Additionally, the disease resistance of this variety has minimized losses due to infections, benefiting both farmers and consumers. The successful adoption of NARC Garlic has helped boost agricultural productivity and food security in the country.
Advantages and Features of NARC G1 Garlic:
High Yield and Improved Quality:
NARC G1 Garlic is known for its high yield potential, which means that farmers can harvest more garlic bulbs per unit area compared to traditional garlic varieties. This increased yield not only translates to higher profits for farmers but also ensures a steady supply of garlic in the market, stabilizing prices for consumers. Moreover, the improved quality of NARC Garlic, with larger and more uniform bulbs, has led to greater consumer acceptance and demand.
Disease Resistance and Pest Tolerance:
One of the key reasons behind the popularity of NARC Garlic is its remarkable disease resistance. This variety shows enhanced resistance to common garlic diseases, such as white rot and purple blotch, which can severely affect traditional garlic crops. By reducing the need for chemical pesticides and fungicides, NARC G1 Garlic promotes more sustainable and eco-friendly farming practices. Additionally, its pest tolerance ensures that the crop is less vulnerable to insect attacks, further improving the overall crop health.
Adaptability to Pakistani Climate and Soil Conditions:
Pakistan has diverse climates and soil types, varying from tropical in the south to temperate in the north. NARC Garlic has demonstrated its adaptability to these diverse conditions, making it suitable for cultivation in various regions across the country. This adaptability has not only expanded the geographical range of garlic cultivation but has also provided opportunities for farmers in regions where garlic cultivation was previously challenging.
Cultivation of G1 Garlic in Pakistan:
G1 Garlic, developed by the National Agricultural Research Center (NARC) in Pakistan, has revolutionized garlic cultivation in the country. Its high yield potential, disease resistance, and adaptability to diverse climates and soil conditions have made it a preferred choice for farmers. Let’s delve into the cultivation process of G1 Garlic in Pakistan in detail:
Selection of Planting Material:
The first step in G1 Garlic cultivation is the selection of high-quality planting material. Healthy and disease-free garlic cloves are essential for obtaining optimal yields. Farmers are encouraged to source the cloves from reliable and certified sources to ensure genetic purity and prevent the introduction of diseases.
Land Preparation:
This Garlic thrives in well-drained and fertile soil. Before planting, the land should be prepared adequately to create a suitable environment for garlic growth. The soil is plowed to break up clods and harrowed to obtain a fine tilth. Proper land preparation ensures good soil aeration and facilitates root development.
Seed Rate:
The recommended seed rate for G1 Garlic in Pakistan is approximately 600 to 800 kilograms of garlic cloves per hectare (kg/ha). Each clove is planted individually, and the seed rate is expressed in terms of the weight of cloves required per hectare.
Planting:
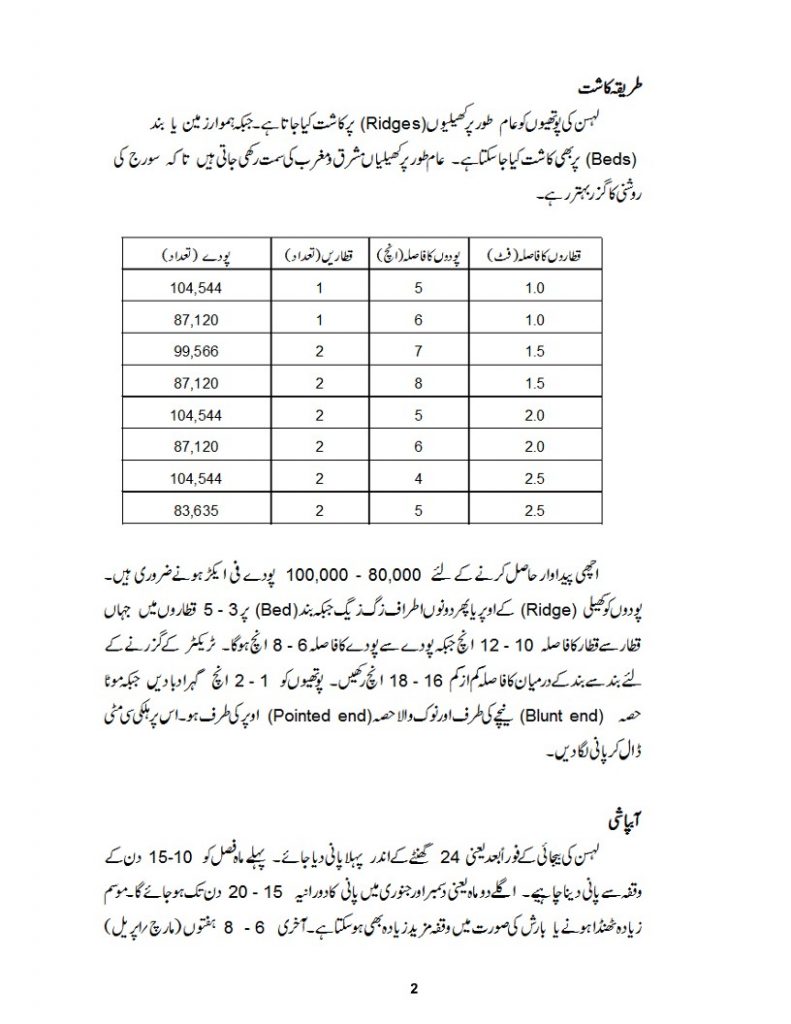
G1 Garlic is typically planted during the autumn season, usually from October to November, as the onset of cooler weather is favorable for bulb development. Cloves are separated from the garlic bulbs and planted individually, with the pointed end facing upwards. The recommended planting depth is around 2 to 3 inches, and the spacing between cloves should be about 6 to 8 inches in rows, with rows spaced about 12 to 18 inches apart.
Fertilizers:
The fertilizer requirement for G1 Garlic depends on the soil’s nutrient content and the specific nutrient needs of the crop. It is essential to conduct soil tests to determine the soil’s nutrient status and the appropriate fertilizer application. Generally, balanced fertilizers with an NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium) ratio of 20:20:20 or 14:14:14 are suitable for garlic cultivation.
For example, based on soil test recommendations, a typical fertilizer rate may be applied as follows:
- Nitrogen (N): 120 to 150 kg/ha = 2 bags Urea
- Phosphorus (P2O5): 120 to 150 kg/ha = 2 bags DAP / 4 bags Ammonium Sulphate
- Potassium (K2O): 120 to 150 kg/ha = 1.5 bags SOP
These nutrient amounts are typically divided into multiple applications during different growth stages of the crop.
Irrigation:
G1 Garlic requires adequate water for proper bulb development, especially during critical growth stages. The number of irrigations needed depends on the local climate, soil moisture retention capacity, and rainfall patterns. Generally, garlic should receive irrigation at the following stages:
- Pre-Planting Irrigation: Garlic beds are irrigated before planting to ensure sufficient soil moisture for germination.
- Early Growth Stage: Garlic needs frequent irrigation during the early growth stage until the roots establish.
- Bulb Formation Stage: During bulb formation, garlic requires consistent and adequate soil moisture to ensure proper bulb development and size.
- Maturation Stage: As the garlic matures, irrigation should be gradually reduced to avoid excess moisture, which can cause bulb rot.
Farmers should consider using efficient irrigation methods such as drip or furrow irrigation to conserve water and provide precise moisture control.
Weed Control:
Effective weed control is necessary to prevent competition for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Farmers can use mechanical methods like hand weeding or inter-row cultivation, along with mulching to suppress weed growth. Care should be taken to avoid damaging garlic plants during weed removal.
Disease and Pest Management:
Crop rotation and use of disease-free planting material can help reduce disease pressure. In case of pest infestations or disease outbreaks, farmers should adopt integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which may include the use of biopesticides or eco-friendly chemicals to minimize environmental impact.
Harvesting:
G1 Garlic is ready for harvest when the garlic leaves start turning yellow and drying out. Harvesting usually takes place from April to May, depending on the local climate and planting time. Care should be taken to avoid damaging the bulbs during harvesting, as this can affect bulb quality and storage life.
Curing and Post-Harvest Handling:
After harvesting, G1 Garlic bulbs need to be cured and dried before storage. Curing involves keeping the garlic bulbs in a well-ventilated area with moderate temperature and humidity for about 2 to 3 weeks. This process helps in reducing moisture content, improving bulb shelf life, and enhancing flavor. Once cured, the bulbs are cleaned and sorted for storage or market.
Storage and Marketing:
Proper storage is essential to preserve the quality of Garlic bulbs. The bulbs should be stored in cool, dry, and well-ventilated conditions to prevent sprouting and minimize the risk of mold growth. Farmers can also explore value addition opportunities, such as garlic processing or making garlic-based products, to extend the market life of their produce and add value to their harvest.
Impact of NARC G1 Garlic on Pakistan’s Agricultural Sector:
Economic Benefits for Farmers:
The adoption of NARC G1 Garlic has significantly increased the income of garlic farmers in Pakistan. With higher yields and better quality, farmers can fetch better prices in the market, thereby improving their overall profitability. Moreover, the disease resistance of this variety has reduced crop losses, saving farmers from financial setbacks caused by pest and disease outbreaks.
Contribution to Food Security:
Garlic is an essential ingredient in Pakistani cuisine, and its demand is consistently high. By increasing garlic production and ensuring a stable supply throughout the year, NARC Garlic has played a crucial role in enhancing food security in the country. Moreover, with the surplus production of garlic, Pakistan has the potential to export this commodity to other countries, contributing to regional food security.
Enhancing Agricultural Export Potential:
The success of NARC G1 Garlic has opened up new opportunities for garlic exports from Pakistan. With improved quality and compliance with international standards, Pakistani garlic has gained recognition in global markets. This not only generates foreign exchange earnings for the country but also promotes Pakistan as a reliable supplier of high-quality garlic in the international trade arena.
Research and Development Efforts Behind NARC G1 Garlic:
Role of National Agricultural Research Center (NARC):
The National Agricultural Research Center (NARC) is a leading research institution in Pakistan dedicated to agricultural development. NARC’s team of scientists, agronomists, and biotechnologists played a vital role in the development of NARC Garlic. The research process involved extensive field trials, genetic studies, and breeding programs to identify and select garlic varieties with superior traits. NARC’s expertise and dedication in agricultural research have been pivotal in bringing about this groundbreaking garlic variety.
Collaborations and Partnerships in Garlic Research:
NARC collaborated with various national and international organizations to support garlic research and development. Collaborations with agricultural universities, research institutes, and agricultural extension services have facilitated knowledge exchange and technology transfer. Additionally, partnerships with international agricultural organizations have allowed NARC to access cutting-edge technologies and expertise in garlic breeding and cultivation.
Future Prospects for NARC G1 Garlic Development:
The success of NARC G1 Garlic has paved the way for continued research and development in garlic cultivation. NARC is likely to focus on further improving the variety through genetic selection and breeding techniques. Additionally, ongoing research may explore ways to enhance the nutritional content and medicinal properties of NARC Garlic, adding more value to the crop.
Market Overview of NARC G1 Garlic in Pakistan:
NARC G1 Garlic has created a significant impact on the garlic market in Pakistan. Since its introduction, it has gained popularity among farmers, traders, and consumers alike. The unique advantages and features of NARC G1 Garlic have positioned it as a preferred choice in the market, leading to increased demand and trade.
Increased Production and Supply:
The adoption of NARC G1 Garlic by farmers has resulted in increased garlic production in Pakistan. With its higher yield potential compared to traditional garlic varieties, there has been a surplus of garlic bulbs in the market. This has led to a more stable supply of garlic throughout the year, reducing seasonal fluctuations in prices and ensuring a steady availability of this essential commodity.
Improved Quality and Consumer Acceptance:
NARC G1 Garlic’s larger and more uniform bulbs have improved its overall quality compared to other garlic varieties available in the market. Consumers value these characteristics as they indicate better taste, enhanced nutritional content, and ease of use in cooking. The improved quality has garnered positive feedback from consumers, encouraging them to choose NARC Garlic over other garlic options.
Export Opportunities:
NARC G1 Garlic’s success has not been limited to the domestic market. Its improved quality, disease resistance, and compliance with international standards have created export opportunities for Pakistani garlic. As a result, Pakistani garlic growers and exporters have been able to tap into international markets, earning valuable foreign exchange for the country.
Market Value and Price Competitiveness:
NARC G1 Garlic’s market value has remained higher compared to traditional garlic varieties due to its superior quality and increased demand. The disease resistance of NARC G1 Garlic has also reduced crop losses, helping to stabilize prices and keep them competitive. Although NARC Garlic might be relatively more expensive to cultivate due to its initial seed cost and technology adoption, its higher yields and better quality justify the investment for farmers.
Challenges and Market Growth:
While NARC G1 Garlic has achieved substantial success, there are challenges that need to be addressed for further market growth. These challenges include:
- Ensuring consistent seed availability and maintaining the genetic purity of NARC G1 Garlic to prevent contamination.
- Addressing storage and post-harvest handling issues to preserve the quality of garlic bulbs during transportation and storage.
- Strengthening market linkages and improving marketing infrastructure to facilitate smooth distribution and trade of NARC Garlic.
- Focusing on branding and promoting NARC G1 Garlic in both domestic and international markets to establish it as a recognized and trusted brand.
Overall, the market for NARC Garlic in Pakistan is promising. As long as efforts are made to address the challenges and build on the variety’s strengths, NARC G1 Garlic is likely to continue contributing positively to the agricultural sector, farmer livelihoods, and the country’s overall economic growth.
Challenges and Solutions in NARC G1 Garlic Cultivation:
Addressing Pest and Disease Management:
While NARC Garlic exhibits better disease resistance compared to traditional varieties, there is always a risk of new pathogens emerging. To tackle this challenge, farmers need to implement integrated pest management strategies, including crop rotation, use of resistant varieties, and timely application of biopesticides or eco-friendly chemicals. Regular monitoring of garlic fields is essential to detect any signs of disease or pest infestations early.
Sustainable Farming Practices:
As with any agricultural crop, sustainability is a critical concern. Farmers cultivating NARC G1 Garlic should adopt sustainable farming practices to minimize the environmental impact of their operations. This includes conserving water through efficient irrigation methods, minimizing chemical inputs, and practicing soil conservation techniques.
Market Access and Price Fluctuations:
While NARC G1 Garlic has opened up export opportunities, farmers may face challenges related to market access and price fluctuations. It is essential for farmers to establish reliable marketing channels and explore options for value addition to garlic products. Diversifying the use of garlic in processed foods or medicinal products can help stabilize prices and reduce dependency on volatile fresh garlic markets.


Source: Garlic in Pakistan (لہسن کی کاشت), Ayub Agricultural Research Institute, Faisalabad, Pakistan
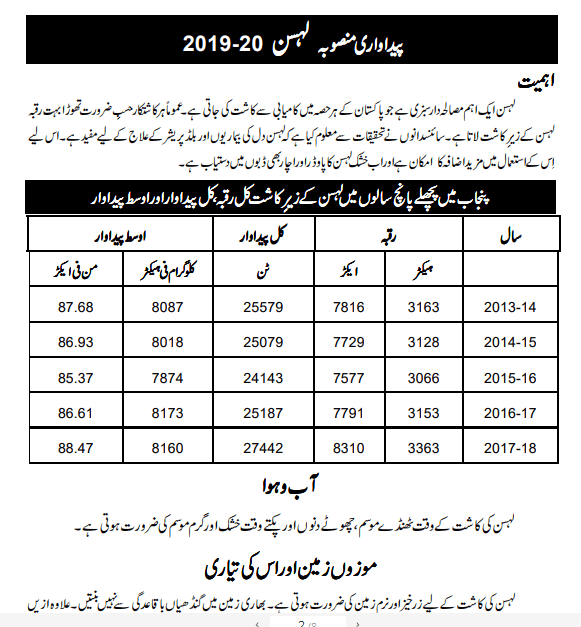
Source 3: Agriculture Department, Government of Punjab, Pakistan
NARC Garlic in Pakistan (لہسن کی کاشت)






