Maximizing Yield and Minimizing Space with Indoor Agriculture

Last updated on June 24th, 2024 at 11:13 am
Table of contents
Urban centers continue growing, but farmland stays the same. This leads to a food production problem – how can we feed more people with no increase in agricultural land area? Indoor Agriculture presents a compelling solution by offering higher yields and greater efficiency through optimized growing environments.
Indoor farming involves growing crops inside enclosed structures like greenhouses or repurposed warehouses using artificial lights instead of sunlight. Indoor farms allow for precise control over variables like temperature, humidity, irrigation, lighting, and nutrition levels. Taking food production into a strictly monitored indoor environment minimizes external risks from pests, diseases, weather, or climate.
Benefits of Indoor Farming
There are several advantages to moving agriculture indoors:
- Higher yields: Crops grown indoors can produce 5-10 times more per square foot compared to traditional outdoor farming. Controlled environments lead to faster growth cycles and year-round production.
- Space efficiency: Vertical farming utilizes tall shelves or stacked layers to multiply the growing area available. Urban centers can repurpose unused buildings into indoor farms.
- Less water usage: Hydroponics and aeroponics provide crops just the right amount of nutrients and moisture precisely when needed, avoiding waste.
- No weather disruption: Indoor farms maintain ideal growing conditions regardless of external climate or seasons.
- Lower transportation: Locating farms near urban centers cuts down on food shipping costs and emissions.
How to Maximize Yield with Indoor Farming
To maximize productivity in an indoor farming operation, it is essential to leverage technologies and techniques that optimize growing conditions, accelerate growth, and boost yields per square foot. A key strategy is employing hydroponics or aeroponics to deliver water, nutrients, and oxygen directly to exposed roots.
This soil-free approach avoids soil-borne diseases, allows closer plant spacing, and enables precise control over moisture and nutrition levels. Investing in LED lights tuned to specific wavelengths can also drive faster photosynthesis. Manipulating the lighting schedules triggers plants to redirect energy into fruiting, flowering, and harvestable plant growth.
Vertical farming makes use of vertical space by stacking plants in layers or on tall shelves. This increases the plant’s capacity in a given floor area. Automating tasks such as seeding, monitoring, and harvesting reduces labor requirements and frees up employees to focus on increasing productivity.
Continuous data collection and analytics enable growers to track growth metrics and optimize the environment by fine-tuning temperature, humidity, lighting, nutrients, and other variables. Strict hygiene and air filtration reduce the risk of pests or pathogens wreaking havoc on yields.
Finally, choosing high-yielding cultivars suited to indoor cultivation, in conjunction with vigilant monitoring and rapid condition adjustments, prevents plant stress and underperformance. Indoor farms can maximize harvests indefinitely by purposefully implementing these technologies, techniques, and practices for high-density optimized production.
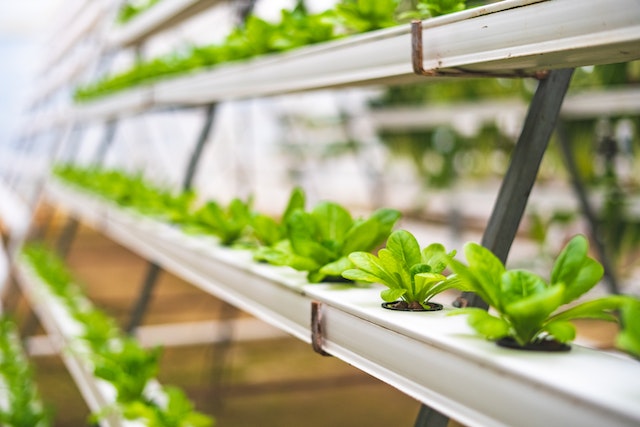

Key Technologies Enabling Indoor Agriculture
- LED lighting: Energy-efficient LEDs mimic ideal light wavelengths for photosynthesis. Lighting schedules can optimize plant growth.
- Hydroponics and aeroponics: Soil-free systems offer direct delivery of water and nutrients to plant roots. This saves space and allows closer plant spacing.
- Automation: Robots, conveyor systems, and AI help automate seeding, harvesting, monitoring, and maintenance for large-scale farms.
- Vertical farming: Shelves or stacked layers with lighting maximize available grow area, multiplying per-square-foot yields.
Realizing the Potential of Indoor Agriculture
While the initial costs of indoor farming are higher, the ability to produce higher yields on smaller plots offers sustainability benefits. Even moving a portion of agriculture indoors could help meet rising food demand.
Indoor farms integrated with urban centers also provide fresher produce while emitting fewer pollutants. With ongoing advancements in lighting, hydroponics, automation, and monitoring technologies, indoor agriculture provides an attainable vision of maximizing food production while using the least amount of space.
Farming’s future may be inside climate-controlled structures rather than in the fields. Indoor farming is a viable option for growing more food on less land in a sustainable and efficient manner. Even though adoption is still in its early stages, interest in indoor agriculture is growing rapidly. Join us as we chart the course of food production in the future.

Summary:
The key takeaway is that indoor farming enables higher yields and greater efficiency through optimized and controlled growing environments. While traditional outdoor agriculture relies heavily on expansion of farmland, indoor farming sustainsably boosts production using vertical space and smart technology.
As global populations grow, indoor farming offers an innovative solution to increase food security, particularly for urban areas. Indoor agriculture comes with higher upfront costs but pays dividends through reliable year-round crop yields, protection from external factors, reduced water usage, and lower transportation needs.
Though still an emerging industry, indoor farming is paving the way for tomorrow’s high-tech and hyper-local food production. With the world needing to produce more using less, the controlled environments of indoor agriculture provide a compelling path to maximize yield while minimizing space.
Click here for more info